Topics Covered in this Article :
What is defect in software development ?
The impact of defects on software development ?
Common causes of defects in software development ?
Strategies for preventing defects in software development
Best practices for detecting and fixing defects in software development
Important Articles related to Bug
What is Defect in software development : Defects in software development can cause serious problems, from lost revenue to damaged reputations. In this guide, we’ll explore what defects are, how they can occur, and what steps you can take to prevent them from happening in the first place. Whether you’re a software developer or a business owner, understanding defects is essential for ensuring the success of your projects.
1. What is defect in software development ?
Software defects, also known as bugs, are errors or flaws in a software program that cause it to behave in unexpected ways or not function as intended. These defects can range from minor issues, such as a misspelled word or a button that doesn’t work, to major problems that can cause the entire program to crash or corrupt data. Defects can occur at any stage of the software development process, from design to testing to deployment, and can be caused by a variety of factors, including human error, coding mistakes, and environmental factors.
2. The impact of defects on software development.
Defects in software development can have a significant impact on the overall project timeline and budget. Fixing defects can be time-consuming and costly, especially if they are discovered late in the development process or after the software has been deployed. Defects can also damage the reputation of the software development team or company, as users may become frustrated with the software’s performance and seek alternative solutions. It’s important to prioritize defect prevention and detection throughout the software development process to minimize the impact of defects on the final product.
3. Common causes of defects in software development.
There are many potential causes of defects in software development, including coding errors, miscommunication between team members, inadequate testing, and unclear requirements. Other factors, such as time constraints and budget limitations, can also contribute to the likelihood of defects. It’s important for software development teams to identify and address these potential causes early in the development process to minimize the risk of defects. This can include implementing clear communication channels, establishing thorough testing protocols, and prioritizing quality assurance throughout the development lifecycle.
4. Strategies for preventing defects in software development.
Preventing defects in software development requires a proactive approach that addresses potential causes early in the development process. One effective strategy is to establish clear communication channels between team members to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding project requirements and goals. Thorough testing protocols should also be implemented to catch any potential defects before they make it into the final product. Additionally, prioritizing quality assurance throughout the development lifecycle can help identify and address potential defects before they become major issues. Finally, it’s important to allocate sufficient time and resources to the development process to minimize the risk of defects caused by time constraints or budget limitations.
5. Best practices for detecting and fixing defects in software development.
Detecting and fixing defects in software development is crucial to ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product. One best practice is to establish a thorough testing process that includes both automated and manual testing. This can help catch any potential defects early on in the development process. Additionally, implementing a code review process can help identify and address any coding errors or issues. It’s also important to prioritize communication and collaboration among team members to ensure everyone is aware of potential defects and working together to address them. Finally, tracking and analyzing data on defects can help identify patterns and areas for improvement in the development process.
6. Important Articles related to Bug
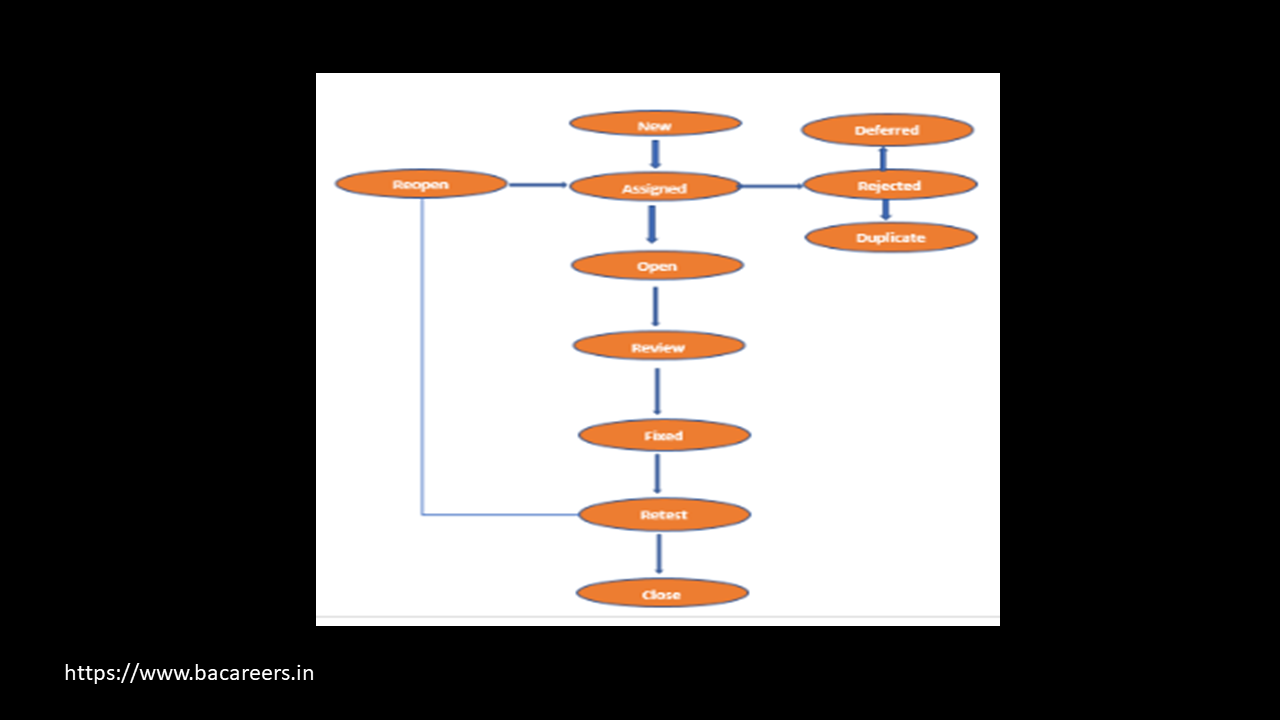
a. Bug Life Cycle / What is Defect Life Cycle ?
b. The Defect Life Cycle Explained
We hope this article provided you the overview on what is defect and how to prevent them.

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.