Organizational modelling is a way to study customer behavior in order to improve service delivery. It helps companies understand their customers’ needs and preferences, which allows them to create products that meet those needs.

Define your customer segments.
Customer segmentation is one of the first steps in creating a model. This involves defining different groups of people based on their buying patterns, demographics, and other characteristics. Once you’ve defined these groups, you’ll need to determine what each group wants and needs. You can use surveys to gather data about your customers.
Identify your target audience.
Once you’ve identified your customer segments, you’ll need to decide who will represent them. You should choose individuals who are knowledgeable about your product or service and who can speak to your brand’s values. These representatives will help you communicate with your customers and build relationships with them.
Create personas.
Personas are fictional characters that represent different groups of people within your organization. They’re used to help you identify what your customers really care about.
Develop scenarios.
Once you’ve identified your customer persona(s), you’ll need to develop scenarios that will help you understand them better. Scenarios are stories that describe real situations where your customers might find themselves. You can use these scenarios to test out ideas, determine whether your product or service would work well in certain situations, and more.
Map out your marketing strategy.
A good place to start when developing your marketing plan is by mapping out your current situation. This includes identifying your strengths and weaknesses as well as what you’re doing now to market yourself. It’s also helpful to think about who your ideal customer is and why he or she should buy from you.
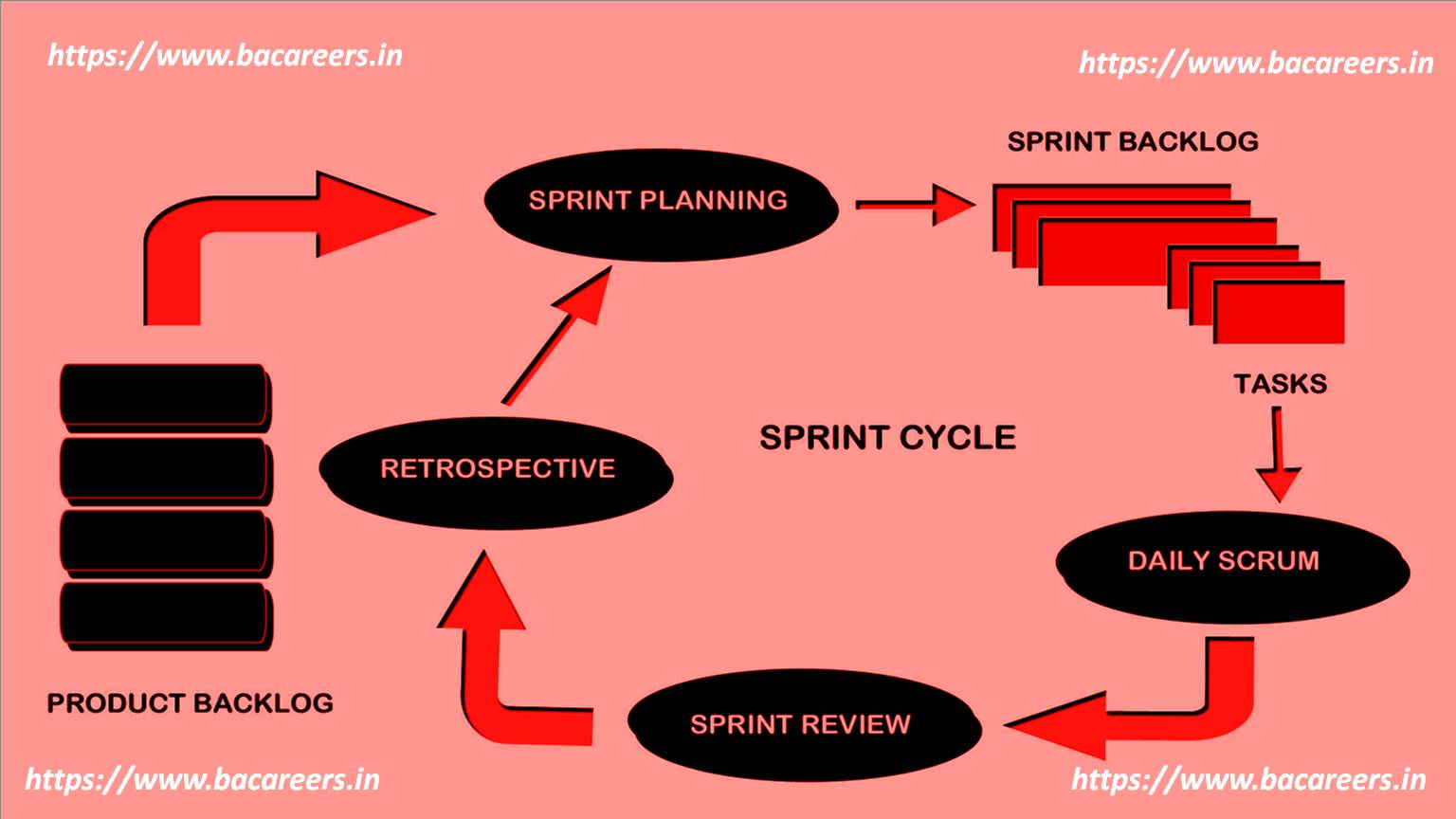
1. Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas is a visual tool that helps us understand how our customers interact with our products and services. It provides a framework for understanding the value proposition of our offering. It is a simple diagram that shows the customer journey, and the different touchpoints along the way.
2. Value Proposition Canvas
A value proposition canvas is similar to a business model canvas, except that it focuses on the value we offer to our customers rather than the product features. A value proposition canvas helps us identify what makes our company unique, and what value we provide to our customers.
3. Customer Journey Map
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the path that customers take to purchase our products and services. We use it to understand where they get stuck, and what their pain points are.
4. Market Segmentation Matrix
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a market into groups based on specific characteristics. In business analysis, we use a matrix to group our potential customers into segments based on their buying behavior. Each row represents a segment, and each column represents a characteristic.
5. Personas
Personas are fictional characters that represent our ideal customer. They help us understand who our target audience is, and what motivates them to buy our products and services.
6. Scenarios
Scenarios are hypothetical situations that help us understand how our customers behave under various conditions. They allow us to test assumptions about how they would react to certain events.
7. Use Cases
Use cases are stories that describe how our customers actually use our products and services. They help us understand how our offerings fit into their daily lives.
1. Business Analysis (BA)
Business analysis is a method of documenting the requirements of a project or program. BA involves gathering information about the customer’s needs, defining those needs, analyzing them, and then developing solutions to meet those needs. In short, BA is a way to ensure that the client gets what they want and that the solution meets their needs.
2. Organizational Modelling
Organizational modelling is a technique used to model the structure of a company. It is a way to understand how the various parts of a company fit together. It is often used to help companies make decisions about organizational changes.
3. Requirements Engineering
Requirements engineering is a discipline that focuses on identifying, capturing, and communicating the requirements of a system. Requirements engineers use techniques like interviews, surveys, and workshops to gather information about the users’ needs. Once the requirements have been identified, they are documented using formal methods.
4. Solution Architecture
Solution architecture is a term that refers to the design of software systems. A solution architect creates a plan for the software system based on the requirements gathered from the user. The solution architect may create a high-level design document that describes the components of the system and how they interact.
5. Software Architecture
Software architecture is the set of rules that govern the creation of software. These rules are created by developers who write code. The goal of software architecture is to ensure that the software works properly and efficiently.
6. System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The system development life cycle (SDLC) is a framework for managing projects. It consists of five major steps: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure. Each step of the SDLC is broken down into smaller tasks.
7. Waterfall Method
Waterfall methodology is a sequential approach to software development. It is a linear process where each phase builds upon the previous phase. The waterfall method is commonly used for large, complex programs.
I hope this article helped you to provide overview on Organizational Modelling .

Business Analyst , Functional Consultant, Provide Training on Business Analysis and SDLC Methodologies.